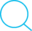
归并排序是建立在归并操作上的一种稳定排序算法,是分治法思想的典型应用。
归并排序主要用于总体无序但各子项相对有序的序列,时间复杂度为 O(nlogn),空间复杂度为 O(n)。
基本思想
1
2
1. 将无序列表分割为n个子序列,每个子序列包含一个元素,子序列可被视为有序序列。
2. 合并多个子序列为一个有序序列,重复此行为直到剩余一个最终有序序列。
将两个有序列表合并成一个有序列表的操作称为二路归并,下面的代码使用二路归并进行归并排序。
代码实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
static List<int> MergeSort(List<int> unsorted)
{
if (unsorted.Count <= 1) return unsorted;
List<int> left = new List<int>();
List<int> right = new List<int>();
int middle = unsorted.Count / 2;
for (int i = 0; i < middle; i++)
left.Add(unsorted[i]);
for (int i = middle; i < unsorted.Count; i++)
right.Add(unsorted[i]);
left = MergeSort(left);
right = MergeSort(right);
return Merge(left, right);
}
static List<int> Merge(List<int> left, List<int> right)
{
List<int> list = new List<int>(left.Count + right.Count);
int leftIndex = 0, rightIndex = 0;
while (leftIndex < left.Count || rightIndex < right.Count)
{
if (leftIndex < left.Count && rightIndex < right.Count)
{
int leftValue = left[leftIndex];
int rightValue = right[rightIndex];
if (leftValue <= rightValue)
{
list.Add(leftValue);
leftIndex++;
}
else
{
list.Add(rightValue);
rightIndex++;
}
}
else if (leftIndex < left.Count)
{
list.Add(left[leftIndex]);
leftIndex++;
}
else if (rightIndex < right.Count)
{
list.Add(right[rightIndex]);
rightIndex++;
}
}
return list;
}
测试程序
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
static void Main(string[] args)
{
List<int> list = new List<int>()
{
324110,-442472,626686,-157678,508681,
123414,-77867,155091,129801,287381,
604242,686904,-247109,77867,982455,
-210707,-922943,-738817,85168,855430,-365580
};
list = MergeSort(list);
foreach (int item in list)
{
Console.Write(item.ToString() + " ");
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
输出结果
1
-922943 -738817 -442472 -365580 -247109 -210707 -157678 -77867 77867 85168 123414 129801 155091 287381 324110 508681 604242 626686 686904 855430 982455